The Relationship Between Folate and Methotrexate – Understanding the Role of Folic Acid in Methotrexate Therapy and its Impact on Patient Health
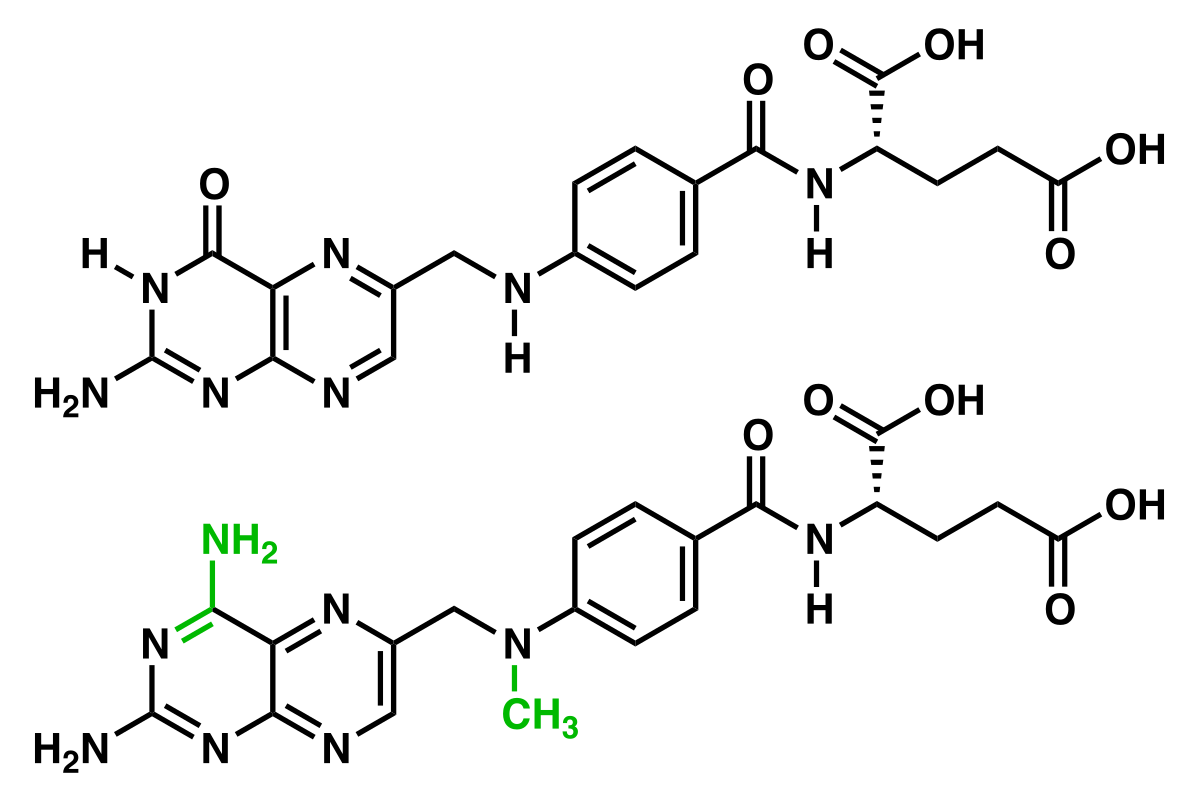
When it comes to the delicate balance of our body’s inner workings, there are few partnerships as powerful as that of folate and methotrexate. These two substances, often spoken of in medical circles, work together to promote optimal health and well-being.
At the center of this dynamic duo is folic acid, a vital nutrient commonly found in a variety of foods. Folic acid is essential for the synthesis of DNA and cell division, playing a crucial role in the growth and development of our body’s tissues. But what makes this nutrient truly remarkable is its ability to support the body in times of stress or illness.
In parallel, methotrexate, a medication with diverse applications, has long been recognized for its benefits in treating certain medical conditions. This powerful drug acts by inhibiting the function of an enzyme that relies on folic acid, effectively reducing the activity of rapidly dividing cells. In doing so, it provides relief for a range of conditions and contributes to improved health outcomes.
When combined, the potential of folate and methotrexate is magnified, offering a comprehensive approach to medical treatment. The unique interplay between these two substances enables a targeted and effective approach, allowing for personalized care and improved patient outcomes.
Folate: An Essential Vitamin for Health and Wellness
Folate is a crucial nutrient that plays a vital role in ensuring overall health and well-being. It is a natural form of vitamin B9 that is essential for various bodily functions. This nutrient promotes proper cell growth and development, aids in the production of DNA and RNA, supports healthy cognitive function, and helps maintain a strong immune system.
|
One of the key benefits of folate is its ability to support the production and maintenance of new cells in the body. This process is particularly important during periods of rapid growth, such as pregnancy and childhood. Folate is vital for the development of the nervous system and is critical for the healthy growth of a fetus. |
|
In addition to its role in cell growth, folate also plays a significant role in the production of DNA and RNA, the building blocks of genetic material. It is involved in the synthesis of nucleotides, the structural units of nucleic acids. Without sufficient folate, this process can be impaired, leading to potential health issues. |
|
Folate is also linked to cognitive function and mental health. It plays a role in the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which are essential for maintaining a balanced mood and optimal cognitive performance. Studies have shown that low folate levels may contribute to an increased risk of depression and cognitive decline. |
|
Furthermore, folate plays a crucial role in supporting a robust immune system. It aids in the production of white blood cells, which are responsible for fighting off harmful pathogens and maintaining overall immune function. Folate deficiency can weaken the immune response, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses. |
To support the body’s folate levels, a healthy and balanced diet is essential. Good sources of folate include leafy green vegetables, legumes, fortified cereals, and citrus fruits. In some cases, supplementation may be required, especially for individuals with specific dietary restrictions or higher nutrient needs.
Overall, folate plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal health and well-being. It is a nutrient that supports cell growth, the production of DNA and RNA, cognitive function, and immune system function. By ensuring adequate folate intake, individuals can promote their overall health and wellness.
The Role of Folate in the Body
Folate plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and proper functioning of the human body. This essential nutrient is involved in several important bodily processes, supporting functions such as cell division, DNA synthesis, and the production of red blood cells.
Key Functions of Folate:
1. Supporting Cell Growth and Repair
Folate is necessary for the growth and repair of cells in the body. It aids in the production of new cells, ensuring that tissues and organs can regenerate and stay healthy. This includes the growth of skin cells, hair follicles, and the linings of the digestive system.
2. DNA Synthesis and Methylation
Folate plays a crucial role in the synthesis and maintenance of DNA. It is involved in the production and repair of DNA, helping to ensure the accuracy of DNA replication. Furthermore, folate is necessary for methylation processes, which involve the addition of a methyl group to DNA, regulating gene expression and overall cellular function.
Folate is not only essential for the growth and development of the body, but it also supports overall health by contributing to the proper functioning of various bodily systems.
In addition to its roles in cell growth, repair, and DNA synthesis, folate plays a key role in red blood cell production. It is necessary for the formation of mature red blood cells, helping to prevent anemia and maintain healthy oxygen levels in the body. Folate also supports the nervous system, aiding in the production of neurotransmitters and supporting proper brain function.
While folate is naturally found in many foods, such as leafy green vegetables, legumes, and citrus fruits, it is also available as a dietary supplement. Adequate folate intake is crucial for overall health, as deficiencies can lead to various health issues and complications.
Folate Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms, and Health Risks
Folate deficiency is a condition that arises when the body does not have an adequate amount of a vital nutrient required for the proper functioning and maintenance of various bodily processes. This deficiency can occur due to several reasons and can lead to a range of symptoms and potential health risks.
Possible Causes
There are various factors that can contribute to a folate deficiency. One possible cause is an inadequate intake of foods rich in folate, such as leafy green vegetables, fruits, beans, and fortified cereals. Additionally, certain medical conditions or medications may interfere with the body’s ability to absorb or utilize folate. Stress, alcohol consumption, and smoking can also deplete folate levels in the body.
Recognizing Symptoms
Folate deficiency can manifest in different ways, and its symptoms can vary from mild to severe. Common symptoms include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, and poor focus or cognitive function. Some individuals may experience digestive issues, such as diarrhea, loss of appetite, or weight loss. In severe cases, folate deficiency can lead to more serious complications, such as anemia, neurological disorders, and birth defects in pregnant women.
It is important to note that these symptoms can be indicative of other health conditions as well, so it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
Early recognition and treatment of folate deficiency are crucial in order to prevent potential health risks and complications associated with this condition.
In the next section, we will explore the potential health risks that can arise as a result of folate deficiency, along with the importance of maintaining optimal folate levels for overall well-being and proper bodily functions.
How to Ensure an Adequate Folate Intake
In this section, we will explore effective strategies to maintain a sufficient level of folate in your body. Folate, also known as vitamin B9, plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, such as cell division and DNA synthesis. By optimizing your folate intake, you can support your overall health and well-being.
1. Incorporate Folate-Rich Foods into Your Diet
One of the best ways to ensure an adequate folate intake is by including folate-rich foods in your daily meals. These foods can provide you with a natural and easily absorbed form of folate. Some examples of folate-rich foods include leafy green vegetables like spinach and kale, citrus fruits, beans, lentils, and fortified cereals.
2. Consider Folate Supplements
In certain cases, it may be necessary to supplement your folate intake. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine if a folate supplement is recommended for you. These supplements are available over-the-counter and can provide an additional source of folate to help meet your daily requirements.
3. Practice Proper Food Preparation and Storage
To preserve the folate content in foods, it is important to adopt proper food preparation and storage techniques. Avoid overcooking vegetables and opt for steaming or lightly sautéing them to retain their folate content. Additionally, store your fruits and vegetables properly to prevent nutrient loss and degradation.
4. Be Mindful of Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with folate absorption and utilization in the body. Therefore, it is advisable to moderate your alcohol intake to ensure optimal folate levels. If you consume alcohol, aim to do so in moderation and consider limiting your intake to support folate absorption.
- Include folate-rich foods such as leafy green vegetables, citrus fruits, beans, lentils, and fortified cereals in your diet.
- Consult with your healthcare provider to determine if a folate supplement is needed.
- Practice proper food preparation and storage techniques to preserve folate content.
- Moderate your alcohol consumption to support folate absorption.
By following these strategies, you can ensure an adequate folate intake and support your overall health and well-being. Although each individual’s folate needs may vary, incorporating these practices into your lifestyle can help promote optimal folate levels.
